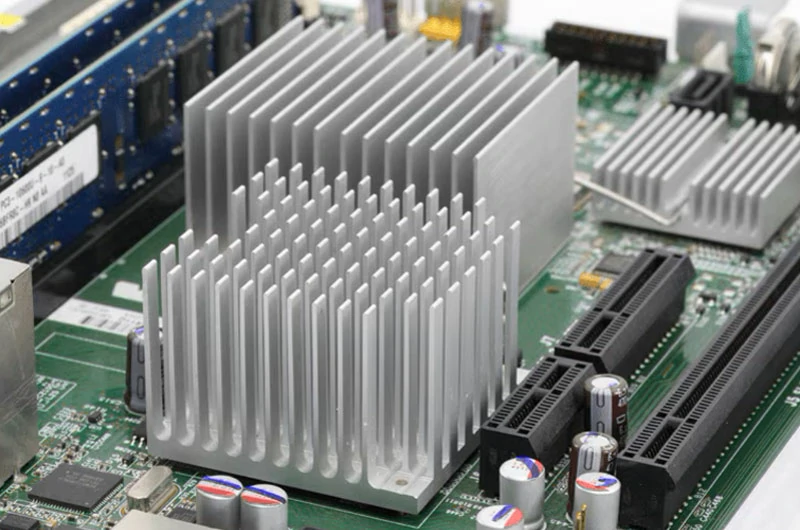
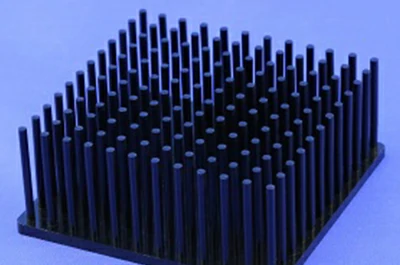
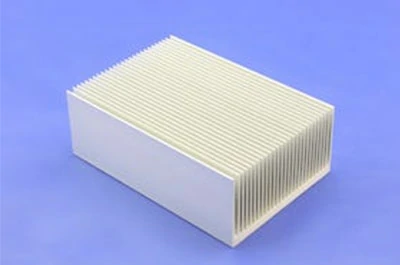
Aluminum heat sink profile specifications
Alloys: 6061, 6063, 6005
Length: 10-6000 mm (customizable for large heat sinks)
Width: 10-500 mm
Common Types: Plate fin type, pin fin type
Common Processes: Extrusion, fin bonding, turning, forging, die-casting
Surface Finish: Anodizing, polishing, electroplating, painting, laser marking, Alodine 5200, Acculabs 628
Colors: Black, silver, blue, red
Processing: CNC machining, cutting, punching, bending, welding, milling, CNC control
Standards: EN 442, ASTM E2112, NAS4122, NAS4121
Certifications: RoHS, CE, SGS, ISO, TUV SUD, UL
Classification of standard aluminum heat sink
Mastar Metal has an extensive stock of standard aluminum radiator profiles in a wide range of sizes and molds.
- Plate Fin Heat Sinks (by the foot)
Plate fin heat sinks are cost-effective and provide optimal thermal performance in forced convection when the fins are parallel to the direction of the airflow.
- 6063-T5 aluminum
- low-cost
- anodized
- customizable in length
- Round PIN-FIN Heat Sinks
Pin fin heat sinks have minimal impact on changes in airflow direction and can provide excellent thermal performance even under high-speed airflow.
- Omnidirectional characteristics
- low airflow resistance
- high heat dissipation efficiency
- Elliptical PIN-FIN Heat Sinks
An elliptical pin heat sink features low thermal resistance and low pressure drop. Air can smoothly pass through while maintaining speed and high pressure.
- Low thermal resistance
- low pressure drop
- high thermal conductivity

- Cross Cut Heat Sinks
Cross-cutting helps break the stagnant air boundary layer formed on extruded fins, generating turbulence and improving thermal performance.
- 6063-T5
- good mechanics
- high heat dissipation
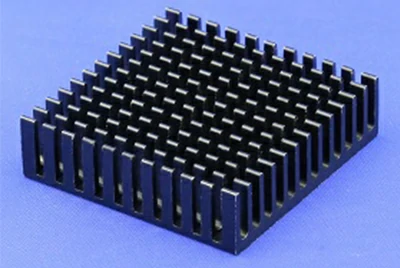
- Sloped fin Heat Sinks
Sloped fin heat sinks have more surface area, resulting in the lowest thermal resistance from the base to the fins, and they are also lightweight.
- More surface area
- high heat dissipation
- easy installation

Classification of custom aluminum heat sinks
We offer custom manufacturing services for specialized shapes or large heat sinks, providing highly personalized solutions for our customers.
- Extruded Aluminum Heat Sink
- Specifications: Can withstand temperatures up to 400°F.
- Applications: Commonly used in computers, lighting, and electrical equipment with power ratings ranging from 15W to 150W and sizes from 2 inches to 3 inches.
 Bonded-Fin Heat Sinks
Bonded-Fin Heat Sinks- Specifications: Can effectively handle temperatures up to 500°F.
- Applications: Bonded fin heat sinks serve equipment with power ratings ranging from 200W to 3kW. Better copper-aluminum bonding.
 Skived Heat Sinks
Skived Heat Sinks- Specifications: Can withstand heat from 300°F to 450°F.
- Applications: Sturdy and durable, ideal for high-power equipment up to 250W in automotive and aerospace applications.
 Forged Heat Sinks
Forged Heat Sinks- Specifications: High-pressure process, with optimal heat dissipation performance.
- Applications: Commonly used in devices such as CPUs.
 Die Cast Heat Sinks
Die Cast Heat Sinks- Specifications: Can handle temperatures from -40°C to 230°C.
- Applications:Diverse in shape, playing a crucial role in LED lighting and automotive electronics.
 CNC Machined Heat Sinks
CNC Machined Heat Sinks- Applications: Commonly used in aerospace components.
- Recommendation: High precision, customizable processing.
 Stamped Heat Sinks
Stamped Heat Sinks- Specifications: Typical thickness is 0.4 millimeters.
- Applications:Suitable for low-power electronic products such as transistors.
- Recommendation:Low cost and easy for mass production and delivery.
 Zipper Fin Heat Sink
Zipper Fin Heat Sink- Specifications: Fin density ranges from 100 to 400 fins per inch.
- Applications: Provides outstanding cooling capacity, making it an ideal choice for aerospace and defense electronic products.
 Heat Pipe Heat Sink
Heat Pipe Heat Sink- Specifications: Heat pipes integrated into the design ensure rapid heat dissipation.
- Applications: Suitable for electronic products with a thermal range of 20W to 150W.
How to choose the alloy grade of aluminum heat sink profiles
| Alloy | Thermal conductivity (W/m-K) | Tensile strength (MPa) | Processability | Anodizing |
| 1050 | 229 | 105 | excellent | Difference |
| 6060 | 175 | 260 | good | good |
| 6061 | 187 | 310 | Excellent (suitable for machining) | good |
| 6063 | 201 | 276 | Excellent (suitable for extrusion) | good |
Services offered by Mastar Metal
- For bulk or repeat orders, Mastar Metal offers the most competitive pricing schemes.
- Mastar Metal provides customization services with the ability to manufacture special shapes and large heat sinks.
- Mastar Metal offers thermal analysis testing services to help evaluate the performance of heat sinks.
- Mastar Metal has ample inventory and a variety of mold sizes to provide quick delivery services.
- Mastar Metal provides samples and shipping.
Applications of aluminum heat sinks
- LED cooling: LED fixtures, LED displays.
- Semiconductor cooling: CPU, GPU, ASIC, military equipment.
- Electric vehicle cooling: Motor controllers, battery packs.
- Electronics: TVs, refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners.
- Electronic components: Power bricks, DSPs, TSOPs, ASICs, DIPs, BGAs, LGAs.
- Communication equipment: Base stations, routers, switches, lasers.
- Medical devices: CT scanners, MRI machines, ultrasound equipment.
- Power generation: Photovoltaic systems, inverters, wind turbines, transformers.
Advantages of aluminum heat sink profiles
- Excellent thermal conductivity
- Low density, lightweight, easy to install
- Non-magnetic, avoids magnetic field interference
- High ductility, easy to process
- Outstanding corrosion resistance
Factors affecting the performance of aluminum heat sinks
Thermal conductivity: The thermal conductivity coefficient measures a material's ability to transfer heat. Materials with higher thermal conductivity have stronger heat transfer capabilities.
Size of the heat sink: Larger heat sinks have a larger surface area, allowing them to dissipate more heat.
Type, number, and arrangement of fins: The type, number, and arrangement of fins on the heat sink can impact its thermal performance. Generally, a higher number of fins, smaller spacing, and tighter arrangement lead to better heat dissipation.
Airflow: Airflow refers to the amount of air passing through the heat sink and is typically measured in cubic meters per second (m³/s). Greater airflow results in more heat being carried away, leading to better heat dissipation.
Surface treatment: Surface treatments of heat sinks can improve their surface emissivity, thereby enhancing heat dissipation efficiency. Common surface treatments for heat sinks include anodizing and coating.
Price of aluminum radiator profiles
- Larger heat sinks typically have higher prices.
- Heat sinks made of more expensive materials have higher prices.
- Heat sinks with more complex surface treatments have higher prices.
- Heat sinks produced using extrusion processes have lower prices. Those made using fin bonding, turning, forging, and die-casting processes have progressively higher prices.
- Generally, the larger the purchase quantity, the lower the unit price.