Mastar-Metal takes you on an in-depth analysis of 20 common aluminum profile connection methods, covering variousangles such as 90°, 45°, 135°, as well as internal and external connections.
Vivid and intuitive videos and animations are used for demonstrations to facilitate understanding and application.
20 Practical Ways to Connect T-Slots (Video)
Discover the best T-Slot connection methods in this video, where we explore various techniques to help you choose the right solution for your project.
1. Internal Connectors
Used for a 90° connection between two profiles, this type of connection is hidden and offers high strength.
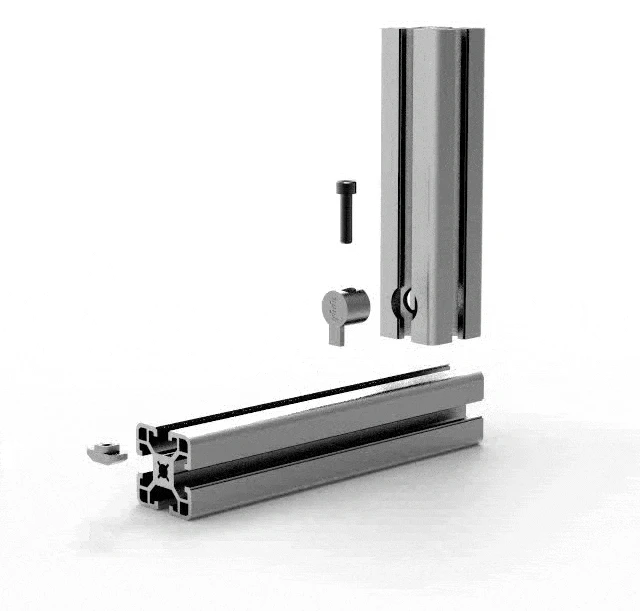

The method of intermediate connection:

2. Angle Bracket (90°, 45°, 135°)
Used for external connection of profiles at fixed angles, available in three angles: 90°, 45°, and 135°, suitablefor securing paneling.
Die-cast Aluminum Corner Joint:

Extruded Aluminum Corner Joint:
45°,135° Connection:
3. Screw Connection
Used for 90° internal connection of two profiles, easy to install and disassemble, commonly used for simple profileenclosure connections.

Different Styles of Screw Connections:

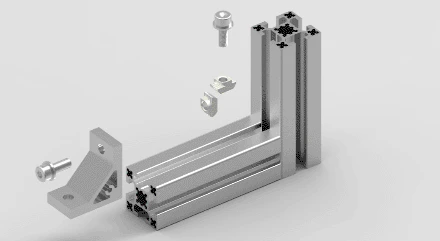
4. L-Shaped Corner Connector (90°)
Used for a 90° connection between two profiles, easy to install and disassemble without additional machining of theprofiles.
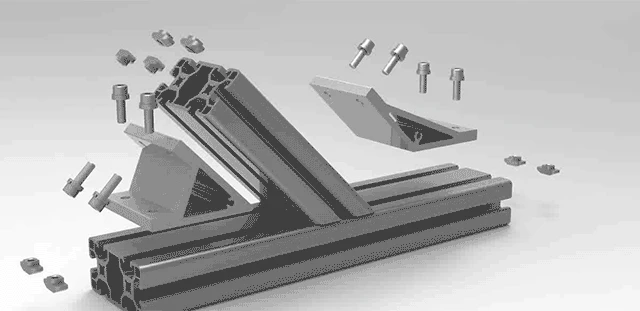
5. High-Strength Angle Slot Connector (45°)
Used for internal connection of two 45° angle profiles, offering high strength and commonly used for securing doorframe profiles.
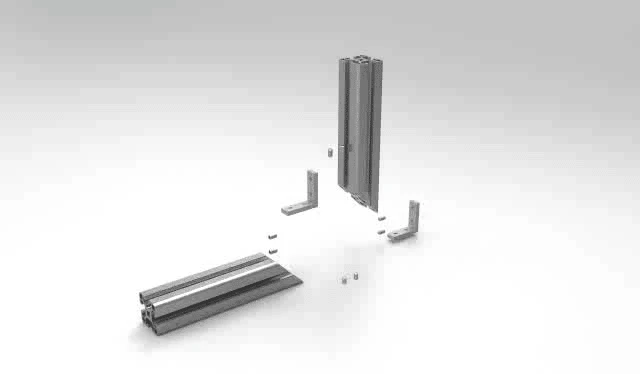
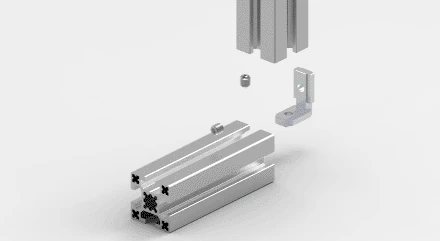
6. End Face Connector
Used for right-angle connection between two or three profiles, providing a firm and aesthetic connection.
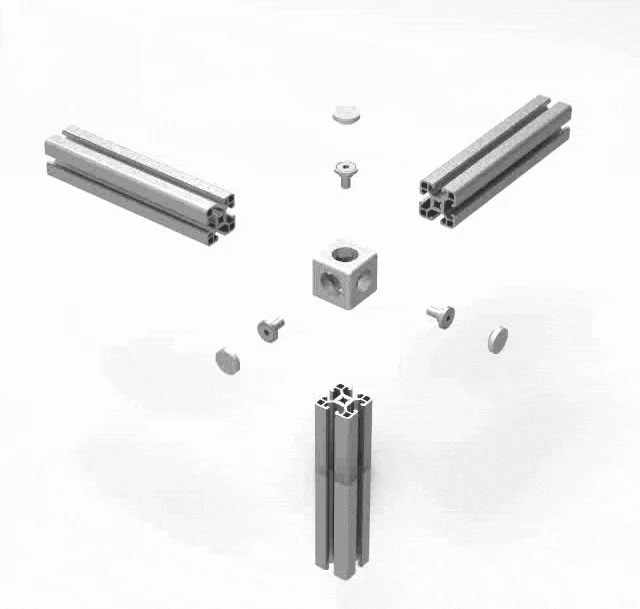

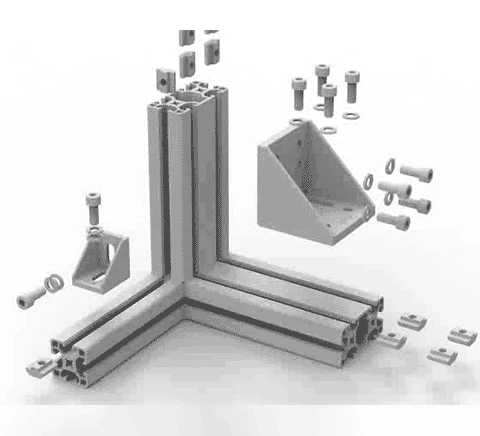
7. Three-Dimensional Connector (Right Angle)
Used for right-angle connection between three profiles, providing convenient and quick assembly.
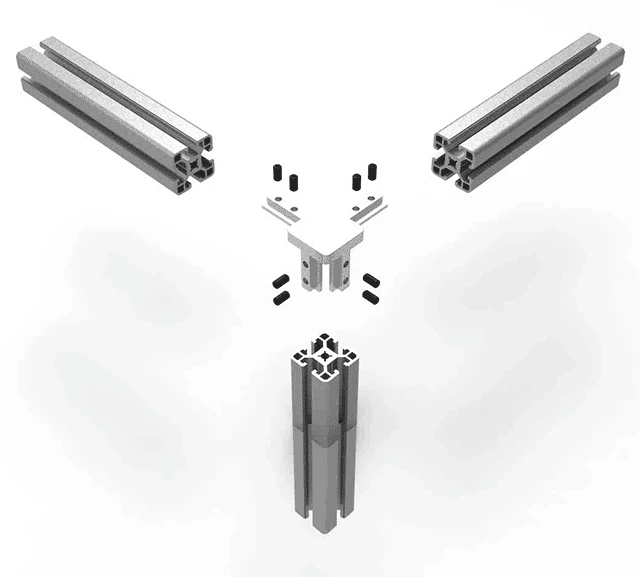
8. Three-Dimensional Connector (R Angle)
Used for right-angle connection between three arc-shaped profiles, providing convenient and quick assembly.
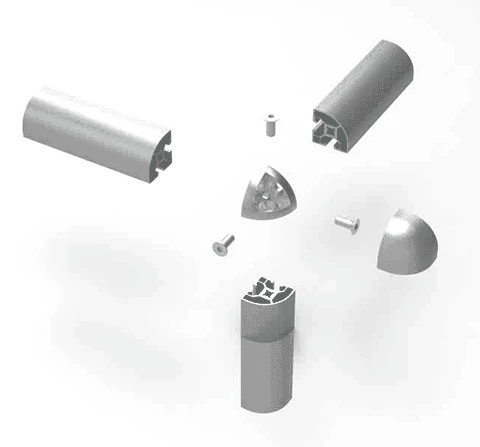
9. Elastic Fastener
Used for 90° internal connection of two profiles, easy to install and disassemble.
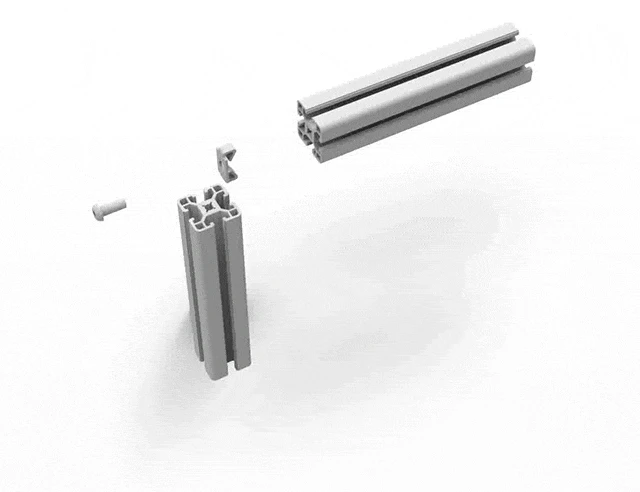

10. End connector
Used for 90° internal connection of two profiles, concealed connection, high connection strength.

11. Cross connector
Used for high-strength coupling of two profiles.
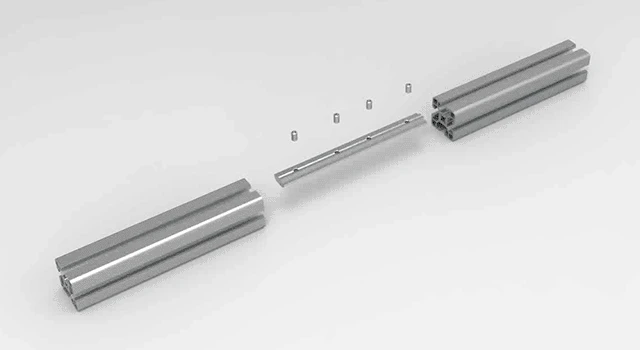
12. Anchor connector
Used for connecting two profiles at various angles, providing a hidden and convenient installation for the profiles.

13. Articulated hinge
Used for connecting two profiles with adjustable angles ranging from 30° to 150°.
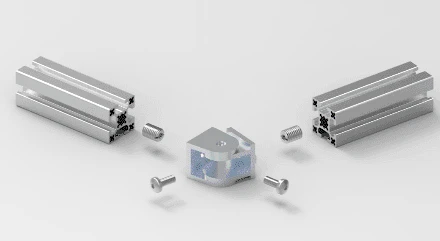
14. Turning connection plate
Used for connecting various profiles and allows for multi-angle rotation.
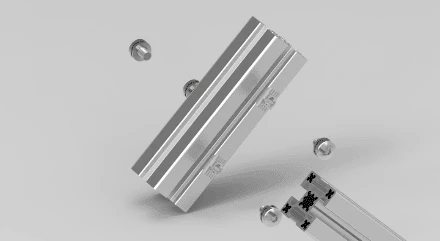
15. Connecting plate
Used for connecting multiple profiles, featuring high connection strength and convenient installation without theneed for profile processing.
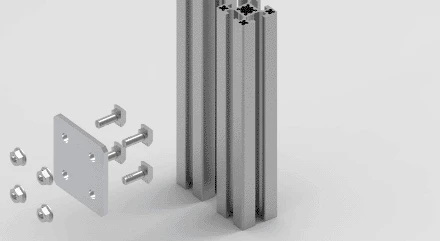
16. Angle connector
Allows for the connection of profiles at any angle.

17. Bolt head assembly
Insert elastic nut into one profile, insert round column into another profile, and secure them using a bolt.
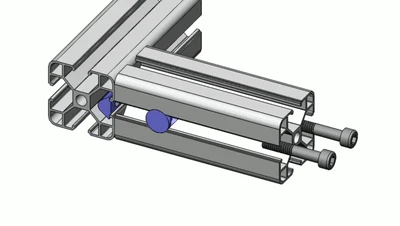
18. Cross-shaped connecting plate
Used for high-strength connection of single-channel profiles in a "+" shape structure.
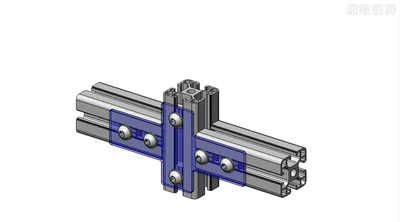
19. L-shaped, T-shaped - external connecting plate
Used for high-strength connection of single-channel profiles in an "L" or "T" shape structure.
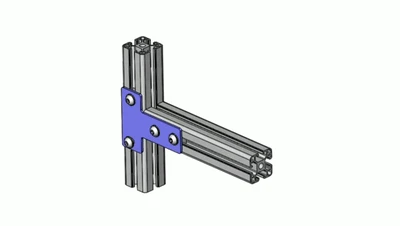
20. Y-shaped - external connecting plate
Used for high-strength connection of single-channel profiles in a "Y" shape structure.
How to Choose the Right T-Slot Connection Method
Application Scenario: Determine the T-Slot's use. Light structures can use simple bolt connections, while heavy or load-bearing structures may need stronger internal connectors or corner brackets.
Load Requirements: Choose based on the weight and stress. For high-load applications, consider reinforced connections like double T connections or thicker connectors.
Adjustment and Flexibility: For frequent adjustments, use bolts or quick-locking devices, which are easy to assemble and disassemble.
Aesthetics: For high visual standards, use concealed internal connectors or corner brackets to maintain a clean appearance.
Best Connection Method
Internal Connectors: Ideal for high-strength and concealed connections.
Bolts and Corner Brackets: Suitable for flexible adjustments or easy assembly and disassembly.
Quick-Locking Devices: Best for rapid assembly and adjustment.
Ultimately, the best choice balances strength, stability, cost, and convenience to meet specific application needs.

