Aluminum tubes, known for their lightweight yet strong characteristics, are experiencing rapid growth in the global market due to their diverse applications and excellent properties. In this guide, I will provide a detailed overview of aluminum tube classifications.
Thickness of aluminum tubing
Aluminum tubing is categorized based on its diameter and wall thickness, leading to the following classifications:
| Type | Outer or Inner Diameter (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Alloy | Temper | Delivery Length (m) |
| Thick-Walled Round Tube | 250-1500 | 5.0-150 | 1070, 1100, 5052, 5154, 5056, 3003 | F, O | 1-6 |
| Thin-Walled Round Tube | 6-120 | 0.5-5.0 | 1070, 1100, 5052, 5154, 5056, 5454, 3003 | H14, H18, O | 1-8 |
| Rectangular Tube | 10-70 | 1.0-5.0 | 1070, 1100, 2024, 6061 | H14, H18, O | 1-8 |
| Droplet-Shaped Tube | 2.7×11.5-115×45 | 1.0-2.5 | 2017, 2024, 6351, 6061 | T6, O | 1-8 |
The manufacturing process of aluminum tubing
Aluminum tubes can be produced by various methods including hot extrusion, cold extrusion, conform extrusion, hot rolling, cold rolling, spinning, cold bending, welding, spiral, coil drawing, bimetal, and bonding.
Hot extrusion
- Use: Suitable for producing thick-walled tubes.
- Wall Thickness Range: Generally 5-35mm; large extrusion presses can produce wall thicknesses over 65mm.
- Features: Formed by extruding aluminum billets at high temperatures (400-500°C), suitable for large diameter and high wall thickness tubes.
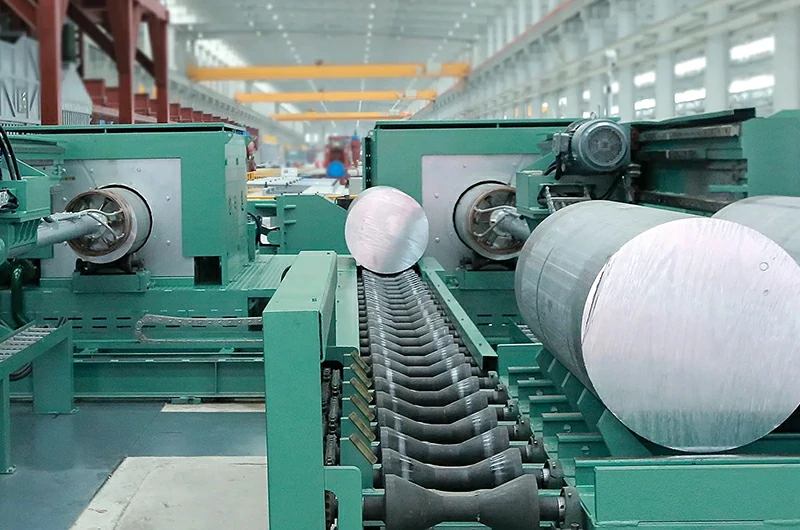

Cold extrusion
- Use: Mainly used for producing thin-walled tubes.
- Wall Thickness Range: Generally 0.5-5mm, suitable for high precision and high strength tubes.
- Features: Extruded at room temperature, using high pressure to form aluminum billets.
Cold rolling
- Use: Used for manufacturing thin-walled tubes.
- Wall Thickness Range: Generally 0.5-5mm.
- Features: Formed by repeatedly rolling at room temperature, achieving desired wall thickness and diameter, suitable for high strength and high surface quality needs.
Cold drawing
- Use: Includes coil drawing, and can produce extremely thin-walled tubes.
- Wall Thickness Range: Can be as thin as 0.1mm or less.
- Features: Formed by drawing at room temperature, increasing the strength and surface smoothness of the tubes.
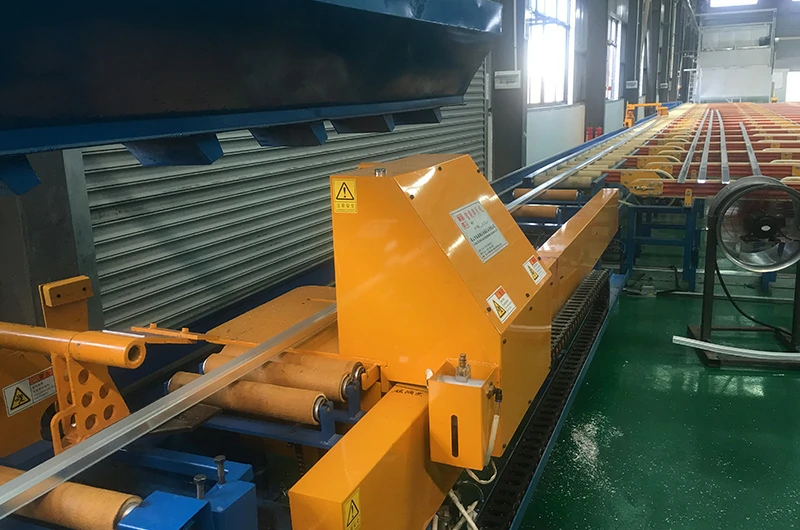

Welding
- Use: Produces welded tubes through cold bending and high-frequency welding.
- Wall Thickness Range: Depends on specific design, generally used for long tubes and complex shapes.
- Features: Suitable for producing complex shapes and long lengths, using high-frequency currents for welding.
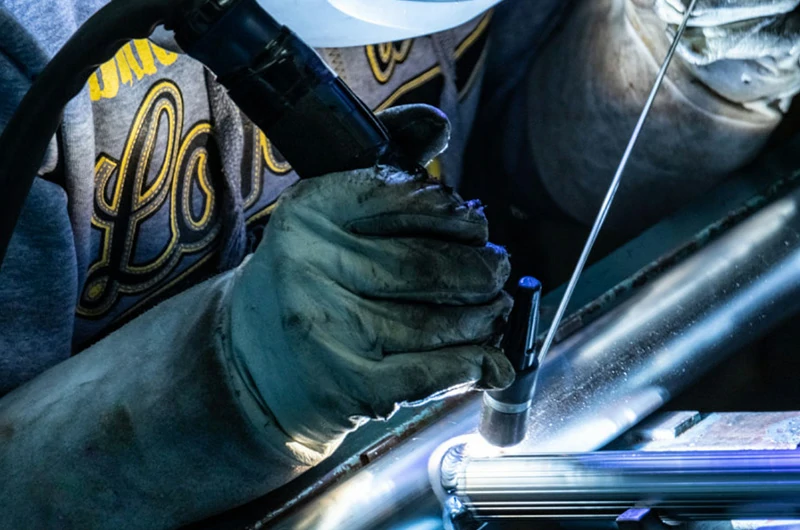

Spinning
- Use: Used for manufacturing extremely thin-walled tubes.
- Wall Thickness Range: Can be as thin as 0.1mm or less.
- Features: Formed by rotating moulds and applying pressure, suitable for high precision and high-quality products.
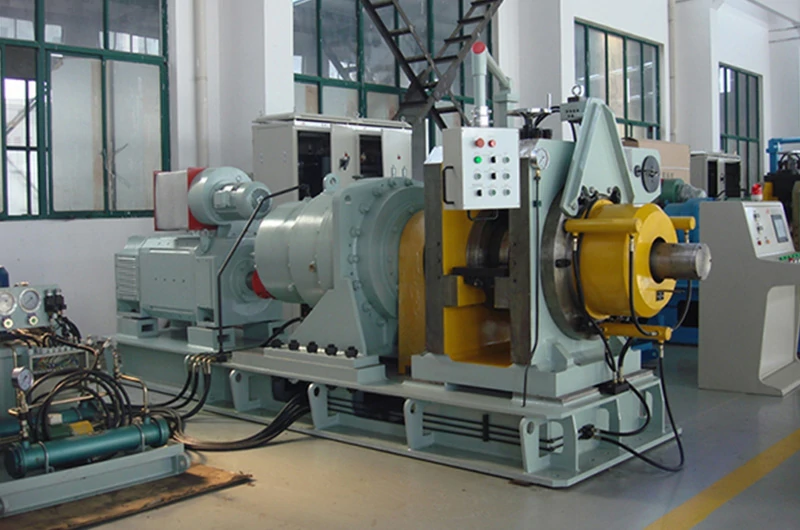
Continuous extrusion
- Use: Produces various shapes and specifications of aluminum tubes.
- Wall Thickness Range: Can produce both thin-walled and thick-walled tubes based on design requirements.
- Features: Suitable for large-scale continuous production, producing aluminum tubes in desired shapes with high process stability.

Cross-sectional shape of aluminum tubing
Aluminum tubes come in various cross-sectional shapes, each serving distinct purposes across different industries.

Fluid transportation: Used in plumbing, pipelines, and HVAC for stress distribution.
Structural components: Integral to scaffolding, frames, and columns.
Automotive and aerospace: Perfect for roll cages, drive shafts, and airframes.

Automotive and bicycle frames: Oval tubes are preferred for their aerodynamic properties and sleek appearance.
Furniture design: They are used in modern furniture for aesthetic appeal and structural integrity.
Heat exchangers: These tubes enhance fluid flow characteristics and heat transfer efficiency.

Droplet-shaped tube
Aerodynamics and hydrodynamics: Ideal for reducing drag in vehicle components, underwater structures, and airfoils.
Heat exchangers: Promotes better fluid flow and enhances heat transfer efficiency.

Architectural components: Used in handrails and structural elements for both aesthetic and functional benefits.
Automotive components: Applied in exhaust systems and chassis parts for improved strength and reduced weight.

Construction: Common in building frames, bridges, and supports due to their high load-bearing capacity.
Furniture: Utilized in metal furniture for a modern look and strength.
Machinery: Used in frames and supports of industrial machinery.

Structural engineering: Preferred for beams, columns, and supports where directional strength is crucial.
Manufacturing equipment: Applied in machine frames and conveyor systems.
Automotive: in chassis and support structure where space constraint exist.

Hexagonal tube
Mechanical structures: Utilized in specific structural applications requiring multi-directional strength.
Decorative elements: Employed in architectural and artistic designs for their unique appearance.

Octagonal tube
Architectural elements: Applied in building facades and decorative columns for their distinct look.
Structural applications: Used where uniform load distribution is essential.

Pentagonal tube
Architectural design: Used in modern structures and furniture for aesthetic appeal.
Custom engineering projects: Employed in specialized engineering applications requiring unique cross-sectional profiles.

Trapezoidal tube
Structural components: Used in applications requiring specific load distribution and strength characteristics.
Aerospace and automotive: Applied in components where aerodynamic efficiency and space utilization are critical.

Ribbed tube
Heat exchangers: Enhances heat transfer by increasing surface area and promoting turbulence.
Reinforced structures: Used in construction and engineering for improved structural integrity and load distribution.
Alloy series of aluminum tubing
Aluminum tubes are available in various alloy series, each offering unique properties and advantages for specific applications.
 1000-series aluminum tube
1000-series aluminum tube- Alloy: 1035, 1050, 1050A, 1060, 1070, 1070A, 1100, 1200
- Temper: F, O, H14, H112
- Used primarily for their excellent corrosion resistance and high thermal and electrical conductivity.
 2000-series aluminum tube
2000-series aluminum tube- Alloy: 2017, 2024, 2A11, 2A12, 2219, 2A14, 2A50
- Temper: T4, T6, F, O, H112
- Known for their high strength and excellent machinability, 2000-series aluminum tubes are ideal for aerospace applications.
 3000-series aluminum tube
3000-series aluminum tube- Alloy: 3003, 3A21
- Temper: F, O, H112, H14, H34
- Features good corrosion resistance and moderate strength, 3000-series aluminum tubes are commonly used in chemical and food industries.
 5000-series aluminum tube
5000-series aluminum tube- Alloy: 5052, 5083, 5086, 5154, 5454, 5456, 5A03, 5A02, 5A05, 5A06
- Temper: F, O, H14, H18, H32, H34, H112
- Noted for their excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments.
 6000-series aluminum tube
6000-series aluminum tube- Alloy: 6351, 6062, 6A02, 6063, 6061, 6005, 6005A, 6262, 6105
- Temper: T4, T6, F, O, H112, T5
- Known for their versatility and balanced properties of strength and corrosion resistance.
 7000-series aluminum tube
7000-series aluminum tube- Alloy: 7075, 7A09, 7A15, 7A04
- Temper: T6, T112, T73, F
- Characterized by their high strength and hardness, making them ideal for aerospace and high-performance applications.
Applications of aluminum tubing
Aluminum tubes are utilized in diverse fields, each application highlighting the material's versatility.
Military and civilian conduits
Used for various types of conduits, providing durable and lightweight solutions for both military and civilian applications.
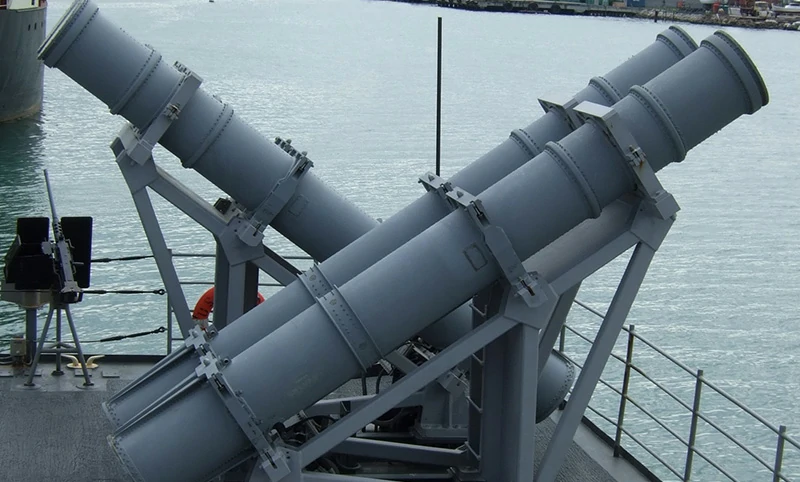

Shell tubes
Essential in munitions and other defence-related applications, offering high strength and reliability.
Container tubes
Utilized in the packaging industry, providing lightweight and corrosion-resistant options for transporting goods.
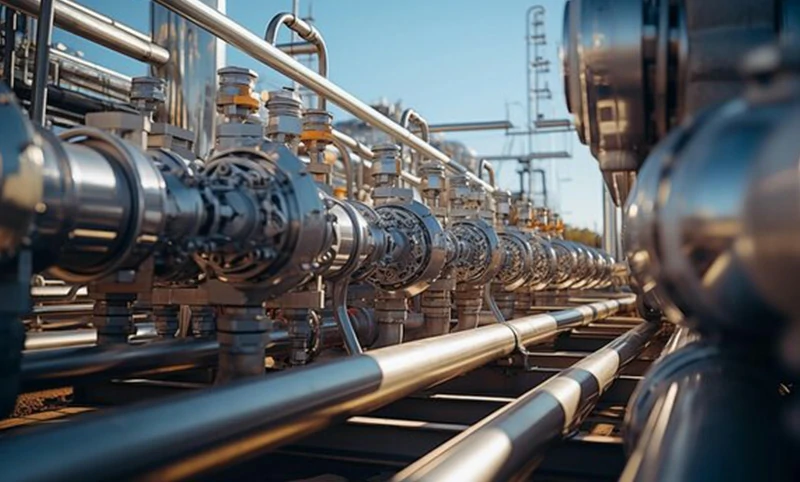

Drilling tubes
Critical in the oil and gas industry, providing strength and durability for deep drilling operations.
Casing tubes
Used in construction and drilling operations, offering support and stability in various applications.
Waveguide tubes
Integral in telecommunications and radar systems, providing efficient pathways for electromagnetic waves.
Heat dissipation tubes
Used in cooling systems to dissipate heat effectively, enhancing the performance and longevity of various devices.
Condenser tubes
Essential in heat exchangers, providing efficient thermal conductivity for various industrial processes.
Evaporator tubes
They are used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, offering high thermal efficiency and durability.
Nozzle tubes
Applied in fluid dynamics, providing precise control and direction for various industrial applications.
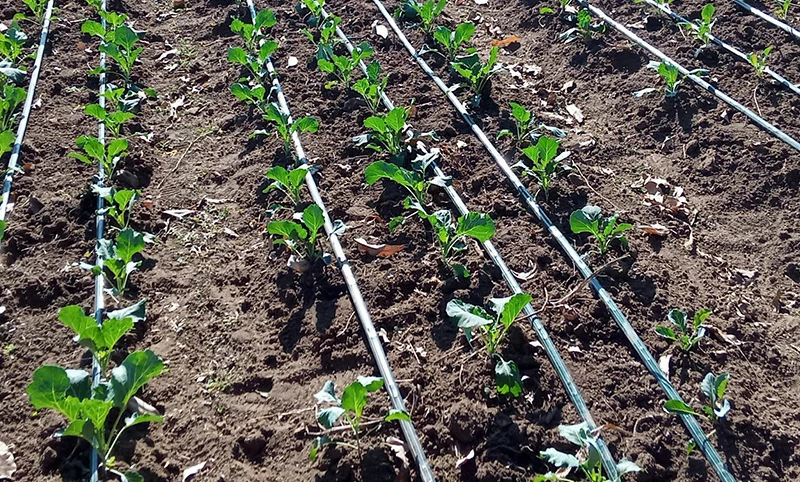
Agricultural irrigation tubes
Used in irrigation systems, providing lightweight and corrosion-resistant solutions for efficient water distribution.

Flagpoles
Aluminum tubes are widely used for flagpoles due to their lightweight, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
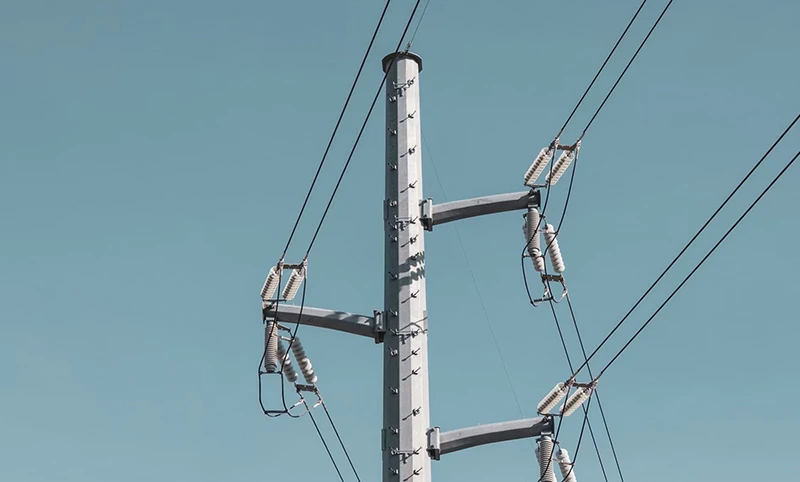
Power poles
They are utilized in the electrical industry, offering lightweight and strong solutions for power distribution.

Pantograph arms
Used in the railway industry, providing reliable and durable components for overhead electrical systems.
Other structural components, decorative tubes, and household items
Aluminum tubes are also used in numerous other applications, from structural components in construction to decorative and household items, showcasing their versatility and adaptability.
FAQs
How to differentiate seamless aluminum tubes and welded aluminum tubes?
| Aspect | Seamless Aluminum Tubes | Welded Aluminum Tubes |
| Manufacturing Process | Manufactured using seamless extrusion technology, achieving one-time moulding. | Produced using ordinary extrusion technology, forming by welding four parts of the aluminum tube together. |
| Weld Lines | Free from weld lines, offering a smoother and more uniform appearance. | It is characterized by four visible weld lines on the cross-section. |
| Raw Material Processing | The surface of the aluminum ingot undergoes turning treatment. | Uses aluminum ingots directly without involving oxide skin treatment. |
| Mechanical Performance | Better pressure resistance and uniform texture. | Slightly poorer mechanical properties. |
| Metal Flow | Exhibits uniform metal flow from start to finish. | Shows uneven metal flow at the start and end of the product. |
| Typical Applications | Ideal for scenarios requiring bending due to their high flexibility and uniformity. | May be prone to cracking when bent, thus less suitable for bending applications. |
| Safety | High safety performance, widely used in international markets. | Potential cracking risks during use, making them less reliable for critical applications. |
Why do precision aluminum tubes require re-processing after extrusion?
Precision aluminum tubes generally need to be re-processed after extrusion through methods like cold drawing and rolling, to achieve tighter tolerances, improved surface finish, and enhanced mechanical properties.
Re-processing ensures that precision aluminum tubes meet the stringent requirements for high-performance applications, such as those in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
The re-processing steps refine the tube's dimensions and improve its overall quality, making it suitable for use in critical applications where precision and reliability are paramount.
Conclusion
Aluminum tubes, with their remarkable properties and diverse applications, continue to be a vital material in various industries. Understanding the classifications is crucial for selecting the right type of aluminum tube for specific applications. As innovations continue to advance, the role of aluminum tubes in technology and industry will undoubtedly expand, driving further growth and development.

