This article will lead you to explore the advantages and disadvantages of forward extrusion and reverse extrusion, and explore their application scenarios in industrial production, process characteristics, and their impact on product quality and production efficiency. A comprehensive analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of these two extrusion processes will help you better understand their applicability in different products and application fields, and provide a more constructive reference for your project needs.
Forward extrusion
Forward extrusion, also known as direct extrusion or forward pressing, is a process in which the metal flows out of the die in the same direction as the applied extrusion force. It is the most economical and widely used extrusion process. Forward extrusion is currently the most widely applied extrusion method, and can be used to produce a variety of solid and hollow aluminum products, such as bars, tubes, and profiles.
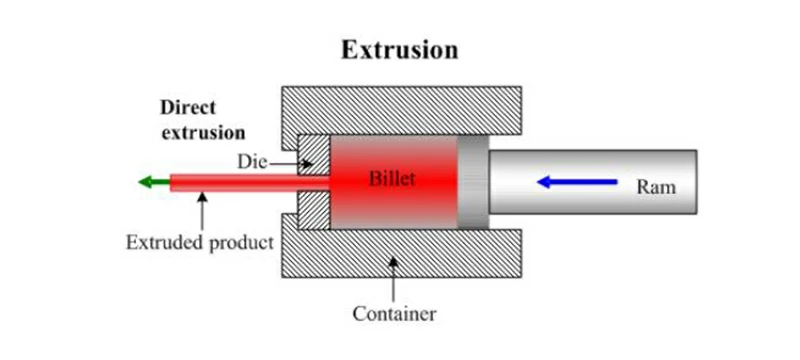
Advantages of forward extrusion
- Low equipment investment: Forward extrusion equipment has mature development, and the required equipment cost is economical.
- High production efficiency: Forward extrusion can produce aluminum semi-finished products in a single extrusion step.
- Low operating cost: The operating cost and energy requirements of forward extrusion in the later production stage are relatively low.
- High product quality: The quality of the final product is subject to the control of the complex production process, and the quality is stable and reliable.
Disadvantages of forward extrusion
- High extrusion force: Powerful equipment is required, and high demands are placed on the rigidity and strength of the equipment.
- High friction loss: Due to the relative motion between the heated billet and the die cavity, the friction force is very high, which leads to energy loss, and a large amount of friction lubricant needs to be used to reduce the friction loss.
- Die cooling: The extrusion die cavity needs to be cooled after each extrusion to reduce the damage to it.
- Uneven distribution of extrusion force: When extruded to the end, the billet becomes thinner, and it must flow radially to adapt to the die, requiring an increased extrusion force, which may lead to uneven distribution of the extrusion force.
- Limitations on product surface quality: Due to the high friction force in forward extrusion, the surface of the aluminum product may have defects.
Common applications of forward extrusion
- Production of aluminum profiles, doors and windows, and pipes for construction materials.
- Production of automotive components, aerospace components, and other mechanical parts.
- Production of electronic components and medical equipment parts.
Backward extrusion
Backward extrusion, also known as indirect extrusion or backward pressing, is a process in which the metal flows out of the die in the opposite direction to the applied extrusion force. Compared to forward extrusion, backward extrusion requires lower extrusion force, higher extrusion speed, and higher dimensional accuracy. It has a significant advantage in the production of seamless hard alloy tubes and bars.
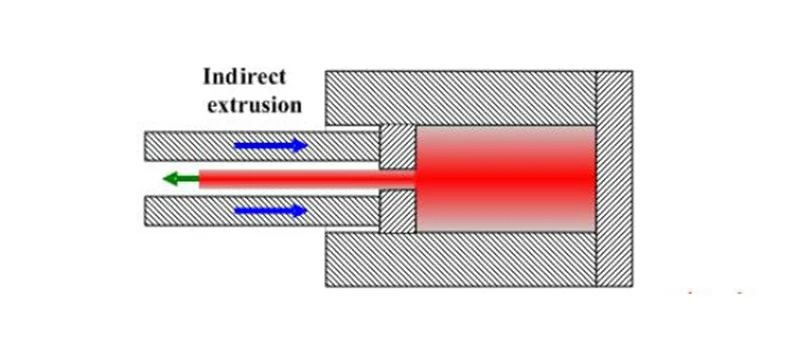
Advantages of backward extrusion
- Lower extrusion force: Compared to forward extrusion, backward extrusion requires 30-40% less extrusion force, which can reduce equipment costs and energy consumption.
- Higher extrusion speed: The extrusion speed of backward extrusion can be increased by 30-50%, resulting in higher production efficiency.
- Uniform metal flow: The metal flow in backward extrusion is more uniform, resulting in better microstructural properties and higher dimensional accuracy.
- Reduced extrusion defects: Due to the uniform metal flow, backward extrusion rarely or never produces defects such as coarse grain rings.
- Higher yield rate: Backward extrusion can reduce scrap, increasing the yield rate by 8-10%.
- Higher precision: Backward extrusion can produce high-precision, high-quality components.
Disadvantages of backward extrusion
- Limited product universality: Backward extrusion is not as versatile as direct extrusion because the cross-sectional area is limited by the maximum size of the die stem.
- Surface defects affecting product appearance: Defects and impurities on the billet surface may affect the surface of the extruded part, impacting the product's appearance.
- Billet surface treatment: To eliminate surface defects on the billet, additional processing such as peeling, grinding, chemical cleaning, or mechanical processing is required.
- Higher equipment investment: The structure of backward extrusion equipment is more complex than that of forward extrusion equipment, resulting in higher equipment investment costs.
Common applications of backward extrusion
- Production of precision parts used in the aerospace, transportation, military, and nuclear industries.
- Production of high-precision, high-quality seamless tubes, bars, and profiles.
- Production of components with stringent surface quality requirements.
Summary
When selecting an extrusion process, the decision should be made based on the specific requirements of the product.
If the product requires high precision, high quality, and stringent requirements on surface quality and microstructural properties, then backward extrusion may be the better choice. Backward extrusion has the advantages of lower extrusion force, higher extrusion speed, uniform metal flow, and reduced extrusion defects, making it particularly suitable for the production of high-end products such as seamless hard alloy tubes and bars.
However, if the product requirements focus more on productivity, cost-effectiveness, and versatility, then forward extrusion may be more suitable. Forward extrusion has the advantages of lower equipment investment and higher production efficiency, making it suitable for large-scale production of aluminum semi-finished products.
Therefore, when selecting the extrusion process, a comprehensive consideration should be made based on the specific requirements of the product and the production situation, in order to achieve the best production results and economic benefits.