Imagine a world where vehicles are lighter and more fuel-efficient, buildings are constructed faster with less waste, and marine vessels glide effortlessly through the water with enhanced performance. This isn't a distant future—it's the reality brought to life by the innovative use of aluminum profiles. Let's dive into 11 fascinating uses of aluminum profiles that highlight their transformative impact across various industries.
1.Automotive lightweight products: categories and features

The automotive industry increasingly uses aluminum alloys to meet demands for fuel efficiency, better performance, and reduced emissions. Here are some key applications:
Battery module end plates
Battery module end plates are integral to the structure of a vehicle, particularly in the battery box. These components include side and end plates of battery modules and are typically made from alloys such as 6061, 6063, 6005, and 6005A.
Aluminum luggage racks and body structural components
Aluminum is widely used in various car body parts, including:
- Roof vent window rails
- Car anti-collision threshold beams
- Bumper beams
- Sunroof frames
- Seat rails
Both hybrid and fully electric vehicles benefit from aluminum battery boxes, thanks to their lightweight and high-strength properties, contributing to overall vehicle efficiency and safety.
Bus and truck body structural profiles
For larger vehicles like buses and trucks, aluminum alloys such as 6063, 6061, 6082, 7003, 7046, and 7H46 are preferred.
Battery pack casing profiles
Battery pack casings include beams, energy absorption boxes, detachment sleeves, and connecting plates. The primary alloys used are 6063, 6061, 6082, 7003, 7046, and 7H46.
2. Revolutionizing pump components with aluminum profiles
Aluminum profiles are ideal for industrial pump components due to their durability and performance. Key uses include:
- Gear pump housing and machine hydraulic gear pumps
- Motor gear pump shell
- Hydraulic pump extrusion
Aluminum alloys like 6061, 6063, 6005, and 7005 offer impressive heat resistance, wear resistance, and air-tightness, making them perfect for creating intricate shapes and handling high mechanical loads.
- Aluminium Profile for Gear Pump Housing & Machine Hydraulic Gear Pumps

- Gear Pump Aluminium Extruded Profile

- Aluminum Extruded Profile for Motor Gear Pump Shell

- Extrusion Aluminium Profile for Hydraulic Pump

- Aluminum Profiles Extrusion for Industrial Hydraulic Gear Pumps

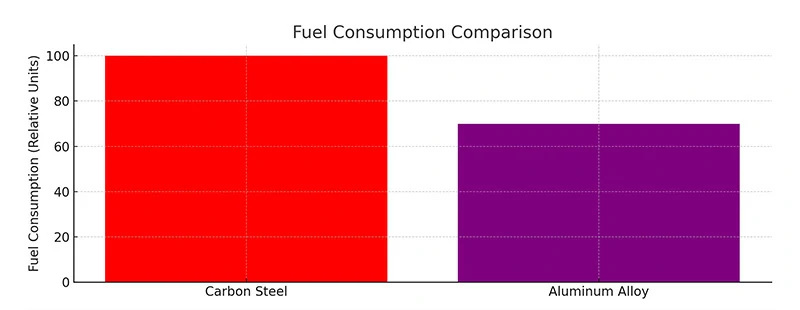
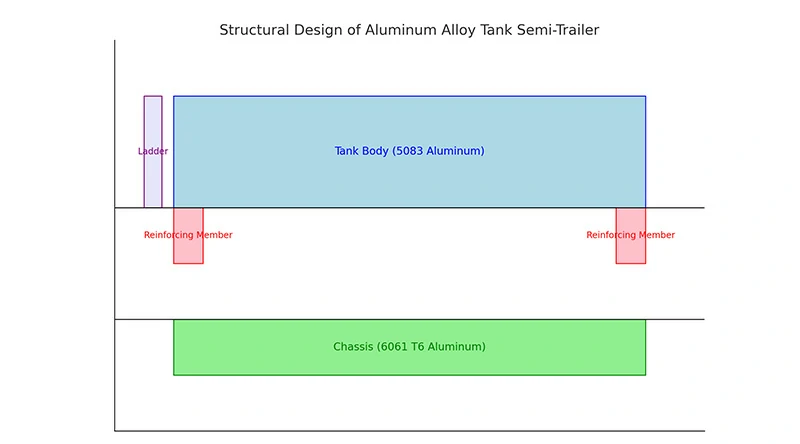
3. Transforming semi-trailers with aluminum profiles
The aluminum profiles used in trailers are primarily from the 6xxx, 3xxx, 5xxx, and 7xxx series of aluminum alloys, with the 6 series (6061, 6005, and 6082) accounting for more than 90%.
Benefits of aluminum alloys
- Stress corrosion resistance: Ensures durability under heavy loads.
- Excellent welding performance: Facilitates easier and stronger joints.
- Corrosion resistance: Prolongs the lifespan of components.
Applications in trailers
- Structural components: Body frame profiles, foundation frame profiles, beams.
- Support parts: Decorative side panels, side columns, grooved wall panels for cargo containers.
4. Application of aluminum profiles in the aerospace industry

Aluminum alloys are widely used in aerospace and are known as "flying metals". Aerospace mainly utilizes the characteristics of high strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys, and profiles are selected according to different parts of aircraft and spacecraft.
Structural components
| Application Area | Description |
| Fuselage Components | High-strength aluminum profiles with high hardness and strength are required for fuselage components, operating systems, compartments, and seats. |
| Engine Room and Air Exchange System | Components near the engine room and air exchange system require heat-resistant profiles to withstand the constant heat generated. |
| Aircraft Wings | Wall panels, beams, stringers, propellers, etc., on the aircraft wings need to be made of corrosion-resistant aluminum profiles. |
Specific aluminum alloys
The aerospace industry uses specific high-strength aluminum alloys, such as:
- 2000 Series (e.g., 2024, 2017): Known for good strength and toughness, used in skins, bulkheads, and ribs.
- 7000 Series (e.g., 7075, 7475): High strength and load-bearing capacity, used in upper wing surfaces and girders.
- 5000 Series (e.g., 5A06, 5052): High corrosion resistance, used in fuel tanks and oil pipes.
5. Reinventing container construction: the power of aluminum profiles

Aluminum profiles are revolutionizing container manufacturing, offering faster, more energy-efficient, and cost-effective production methods.
Benefits of using aluminum containers
| Benefit | Description |
| Significant Weight Reduction | Transitioning from steel to aluminum cuts container weight by 41.2%, enhancing transportation efficiency. |
| Enhanced Fuel Efficiency | Lighter containers reduce fuel consumption, lowering operational costs. |
| Improved Payload Capacity | Reduced weight allows for more cargo, optimizing shipping logistics. |
| Superior Corrosion Resistance | Aluminum's resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of containers, minimizing maintenance needs. |
| Optimized Strength and Durability | Advanced materials and design ensure aluminum containers are strong and durable. |
Mastar application
Companies like Mastar lead this transformation by using advanced aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 6082, to replace traditional steel components. These alloys, especially when treated to T6 conditions, provide impressive strength and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for container applications.
6. Navigating new waters: the impact of aluminum profiles in marine engineering

The advantages of aluminum in marine applications
Aluminum alloys such as 5052 and 5083 are particularly favoured in marine engineering due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratios. These alloys are ideal for applications where reducing the weight of the vessel is crucial, such as in the deckhouse or superstructures.
The use of aluminum significantly lowers the overall weight of the ship, leading to improved fuel efficiency and performance, and a superior strength and weight ratio.
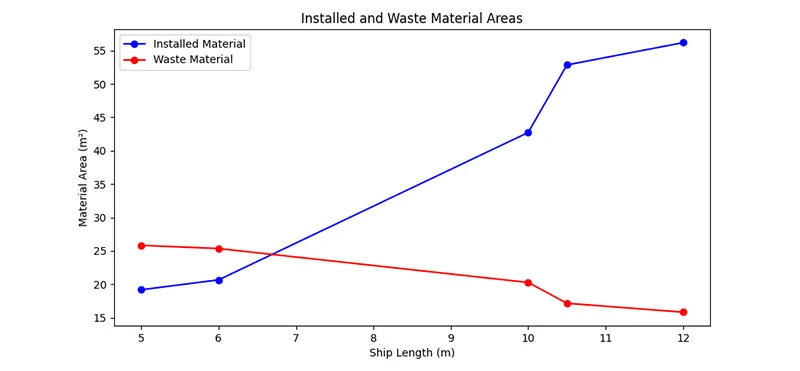
Key applications
- Structural components in large ships and luxury yachts.
- Weight reduction and stability enhancement.
7. Application of aluminum profiles in rail transit industry

Aluminum profiles are extensively used in rail transit, enhancing performance and efficiency:
Urban rail transit
Urban rail transit systems, including subways and light rail, utilize aluminum profiles in various components to enhance performance and efficiency:
| Component | Description |
| Carriages | Aluminum alloy carriages are lighter, reducing energy consumption for acceleration and braking. |
| Conductive Bus Bars | Aluminum is used for its excellent electrical conductivity. |
| Luggage Racks and Windows | Lightweight and durable aluminum profiles are ideal for these interior components. |
High-speed rail
High-speed trains, which operate at speeds exceeding 200 km/h, have stringent requirements for lightweight, airtight, and corrosion-resistant materials. Aluminum profiles meet these needs and are used in:
| Component | Description |
| Railway Carriages and Car Bodies | Aluminum reduces the overall weight, enhancing speed and fuel efficiency. |
| Luggage Racks | Lightweight aluminum profiles contribute to the train's efficiency. |
| Track Profiles | Aluminum profiles are used in the construction of tracks due to their durability and strength. |
Advantages of aluminum profiles in rail transit
| Advantage | Description |
| Weight Reduction | Aluminum profiles are significantly lighter than steel, reducing the energy required for train operation and improving fuel efficiency. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Aluminum's resistance to corrosion ensures a longer service life for rail components. |
| Strength and Durability | High-strength aluminum alloys provide the necessary structural integrity while maintaining a lightweight profile. |
| Cost Efficiency | Aluminum profiles are easier to produce and assemble, reducing manufacturing costs and maintenance requirements. |
8. Harnessing the wind with aluminum profiles in wind turbines

Aluminum profiles are at the forefront of advancing wind energy technology, offering unparalleled benefits that enhance the efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness of wind turbines.
| Benefit | Description |
| Corrosion Resistance | Aluminum's inherent resistance to corrosion makes it exceptionally suited for outdoor and marine environments, ensuring longevity and reducing maintenance costs, crucial for the reliable operation of wind turbines. |
| Lightweight Properties | Aluminum is much lighter than steel or other metals, reducing the overall weight of the wind turbine, allowing for easier installation, and reducing the load on the turbine structure. |
| Superior Tensile Strength | Aluminum has a good strength-to-weight ratio, providing sufficient tensile strength for structural applications while keeping the weight low. |
| Ease of Fabrication | Aluminum is easy to shape, cut, and mould, facilitating the manufacturing process of wind turbine blades, and allowing for more intricate and aerodynamic designs. |
| Availability and Cost-Effectiveness | Aluminum is widely available and relatively inexpensive compared to some advanced composite materials, making it a cost-effective option for manufacturing wind turbine blades. |
| Efficiency | The lightweight nature of aluminum contributes to better efficiency in terms of energy conversion, as the blades can start rotating with lower wind speeds. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | The lower cost and ease of fabrication make aluminum an attractive option for small-scale and experimental wind turbines, balancing initial investment with performance. |
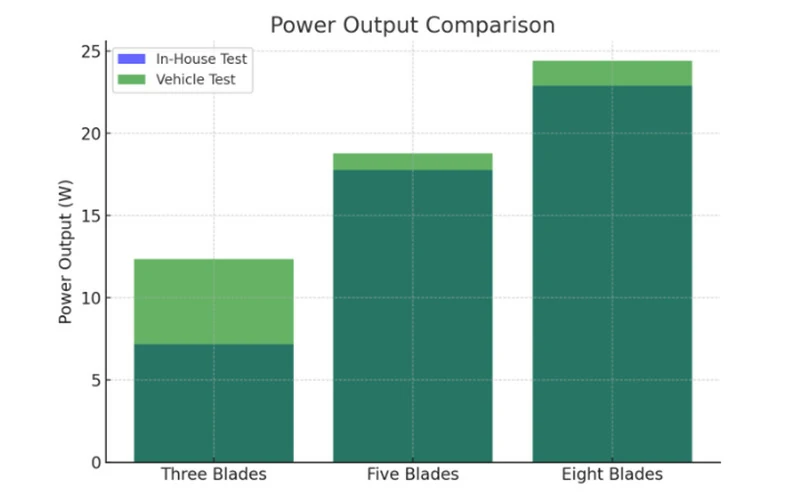
By harnessing the unique properties of aluminum and utilizing alloys such as 6061, 6063, 5083, and 5052, the wind energy sector can achieve greater performance and sustainability, paving the way for a more resilient and efficient energy future.
9. The crucial role of aluminum profiles in photovoltaic systems

The integration of aluminum profiles in photovoltaic systems marks a significant leap forward in solar technology. By leveraging the unique properties of aluminum alloys, manufacturers can produce more efficient, durable, and cost-effective solar panels and mounting systems.
Key benefits of aluminum in photovoltaic systems
Lightweight and durable
Aluminum's lightweight nature makes it easier to handle and install, reducing labour costs and installation time. Despite its lightness, aluminum is incredibly durable, which ensures the longevity of solar panels and mounting structures.
Superior corrosion resistance
Aluminum's resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for outdoor use, where solar panels are exposed to various weather conditions. This property extends the lifespan of the panels and reduces maintenance needs, ensuring reliable performance over time.
Practical applications
- Support structures and frames: Aluminum provides the strength needed to support solar panels while being easy to fabricate and assemble.
- Structural parts in solar cells: Hypereutectic Al-Si alloys are used for their durability and resistance to wear and corrosion.
10. Applications of aluminum profiles in the military sector

Aluminum profiles are widely utilized in the military sector due to their light weight, strength, and corrosion resistance, which enhance the performance, mobility, and reliability of military equipment while reducing weight and energy consumption. Here are the key applications:
Military vehicles
Aluminum profiles are integral to the chassis and body structure of military vehicles such as tanks and armoured vehicles. Their use helps to:
| Application | Description |
| Reduce Overall Weight | Enhancing flexibility and mobility. |
| Improve Performance | Contributing to better fuel efficiency and maneuverability. |
Weapon systems
Aluminum profiles are used in the manufacture of various weapon systems, including:
| Application | Description |
| Artillery and Missile Launchers | Improving portability and reliability. |
| Rocket Engines | Offering lightweight and durable solutions for critical components. |
Warships and submarines
In naval applications, aluminum profiles support the hull structure, deck, and internal equipment.
Benefits of aluminum profiles in military applications
| Benefit | Description |
| Lightweight | Essential for improving the endurance and maneuverability of military equipment. |
| High Strength | Ensures structural integrity and performance under demanding conditions. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Extends the service life of equipment, reducing maintenance costs. |
| Ease of Fabrication | Aluminum alloys are easy to forge, roll, punch, and cut, making them suitable for various military applications. |
11. The impact of aluminum profiles on pedestrian bridges

Aluminum profiles are revolutionizing pedestrian bridge construction, offering unmatched benefits:
- Weight reduction: Lighter structures for easier installation.
- Corrosion resistance: Low maintenance costs.
- Durability: High resistance to environmental factors.
| Comparison of bridge types | |||
| Aspect | Aluminum Alloy Bridge | Traditional Steel Bridge | Traditional Concrete Bridge |
| Material Properties | Lightweight High strength Corrosion-resistant Recyclable | High strength Susceptible to corrosion Heavier than aluminum | Very strong and rigid Heavy Not recyclable |
| Construction Methods | Prefabrication in large sections Quick on-site assembly Minimal disruption | Prefabrication is possible but heavier. More complex assembly due to weight | Cast-in-place Long construction time High disruption |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance costs due to corrosion resistance | High maintenance costs due to corrosion protection needs | Moderate maintenance costs Periodic inspection and repairs needed |
| Durability | High durability Resistant to environmental factors | Durable but requires regular maintenance to prevent rust | Highly durable Can suffer from cracking and spalling over time |
| Impact on Urban Traffic | Minimal disruption due to quick installation | Moderate disruption due to heavier components and longer assembly times | Significant disruption due to lengthy construction processes |
| Environmental Impact | Lower due to recyclability and minimal maintenance | Higher due to regular maintenance and potential environmental hazards | Moderate due to construction materials and methods |
| Installation Methods | Segmented assembly with aerial installation Ground assembly with overall lifting | Heavy lifting equipment needed Complex on-site welding and bolting | Requires formwork and scaffolding Complex and lengthy installation |
| Historical Development | Newer technology with rapid advancements | Well-established with a long history of use | Traditional and widely used Slower to innovate |
Conclusion
In summary, aluminum profiles are not merely components but enablers of future innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. Their growing significance across diverse industries underscores their transformative impact and the endless possibilities they present for the future.

